|
| 1 | +3108\. Minimum Cost Walk in Weighted Graph |
| 2 | + |
| 3 | +Hard |
| 4 | + |
| 5 | +There is an undirected weighted graph with `n` vertices labeled from `0` to `n - 1`. |
| 6 | + |
| 7 | +You are given the integer `n` and an array `edges`, where <code>edges[i] = [u<sub>i</sub>, v<sub>i</sub>, w<sub>i</sub>]</code> indicates that there is an edge between vertices <code>u<sub>i</sub></code> and <code>v<sub>i</sub></code> with a weight of <code>w<sub>i</sub></code>. |
| 8 | + |
| 9 | +A walk on a graph is a sequence of vertices and edges. The walk starts and ends with a vertex, and each edge connects the vertex that comes before it and the vertex that comes after it. It's important to note that a walk may visit the same edge or vertex more than once. |
| 10 | + |
| 11 | +The **cost** of a walk starting at node `u` and ending at node `v` is defined as the bitwise `AND` of the weights of the edges traversed during the walk. In other words, if the sequence of edge weights encountered during the walk is <code>w<sub>0</sub>, w<sub>1</sub>, w<sub>2</sub>, ..., w<sub>k</sub></code>, then the cost is calculated as <code>w<sub>0</sub> & w<sub>1</sub> & w<sub>2</sub> & ... & w<sub>k</sub></code>, where `&` denotes the bitwise `AND` operator. |
| 12 | + |
| 13 | +You are also given a 2D array `query`, where <code>query[i] = [s<sub>i</sub>, t<sub>i</sub>]</code>. For each query, you need to find the minimum cost of the walk starting at vertex <code>s<sub>i</sub></code> and ending at vertex <code>t<sub>i</sub></code>. If there exists no such walk, the answer is `-1`. |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | +Return _the array_ `answer`_, where_ `answer[i]` _denotes the **minimum** cost of a walk for query_ `i`. |
| 16 | + |
| 17 | +**Example 1:** |
| 18 | + |
| 19 | +**Input:** n = 5, edges = [[0,1,7],[1,3,7],[1,2,1]], query = [[0,3],[3,4]] |
| 20 | + |
| 21 | +**Output:** [1,-1] |
| 22 | + |
| 23 | +**Explanation:** |
| 24 | + |
| 25 | +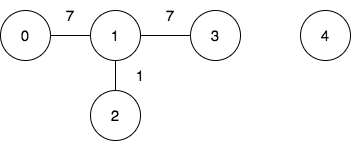 |
| 26 | + |
| 27 | +To achieve the cost of 1 in the first query, we need to move on the following edges: `0->1` (weight 7), `1->2` (weight 1), `2->1` (weight 1), `1->3` (weight 7). |
| 28 | + |
| 29 | +In the second query, there is no walk between nodes 3 and 4, so the answer is -1. |
| 30 | + |
| 31 | +**Example 2:** |
| 32 | + |
| 33 | +**Input:** n = 3, edges = [[0,2,7],[0,1,15],[1,2,6],[1,2,1]], query = [[1,2]] |
| 34 | + |
| 35 | +**Output:** [0] |
| 36 | + |
| 37 | +**Explanation:** |
| 38 | + |
| 39 | +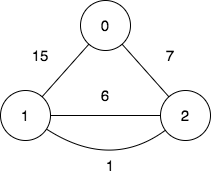 |
| 40 | + |
| 41 | +To achieve the cost of 0 in the first query, we need to move on the following edges: `1->2` (weight 1), `2->1` (weight 6), `1->2` (weight 1). |
| 42 | + |
| 43 | +**Constraints:** |
| 44 | + |
| 45 | +* <code>2 <= n <= 10<sup>5</sup></code> |
| 46 | +* <code>0 <= edges.length <= 10<sup>5</sup></code> |
| 47 | +* `edges[i].length == 3` |
| 48 | +* <code>0 <= u<sub>i</sub>, v<sub>i</sub> <= n - 1</code> |
| 49 | +* <code>u<sub>i</sub> != v<sub>i</sub></code> |
| 50 | +* <code>0 <= w<sub>i</sub> <= 10<sup>5</sup></code> |
| 51 | +* <code>1 <= query.length <= 10<sup>5</sup></code> |
| 52 | +* `query[i].length == 2` |
| 53 | +* <code>0 <= s<sub>i</sub>, t<sub>i</sub> <= n - 1</code> |
| 54 | +* <code>s<sub>i</sub> != t<sub>i</sub></code> |
0 commit comments