-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 58
gif in the README #1
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
Comments
|
Fixed by 9126a70. |
|
When holoviz/holoviews#1977 and holoviz/holoviews#2260 are fixed we can add a script that will reproduce these images. ATM I used LICEcap + Photoshop to edit them. This is the code: %%output fps=5
offset = random.uniform(-0.3, 0.3)
def f(x, offset=offset):
a = 0.01
return x + a**2 / (a**2 + (x - offset)**2)
learner = adaptive.Learner1D(f, bounds=(-1, 1))
def plot(learner):
learner2 = adaptive.Learner1D(f, bounds=learner.bounds)
xs = np.linspace(*learner.bounds, len(learner.data))
learner2.add_data(xs, map(f, xs))
return (hv.Scatter(learner.data)[-1:1, -1:1].relabel('adaptive')
+ hv.Scatter(learner2.data).relabel('homogeneous grid')).cols(1)
plots = []
for i in range(100):
xs, _ = learner.choose_points(1)
learner.add_data(xs, map(learner.function, xs))
plots.append((i+1, plot(learner)))
hv.HoloMap(plots, kdims=['N points']).collate()def ring(xy):
import numpy as np
x, y = xy
a = 0.2
return x + np.exp(-(x**2 + y**2 - 0.75**2)**2/a**4)
learner = adaptive.Learner2D(ring, bounds=[(-1, 1), (-1, 1)])
import itertools
def plot(learner):
learner2 = adaptive.Learner2D(ring, bounds=learner.bounds)
xs = np.linspace(*learner.bounds[0], learner.n**0.5)
ys = np.linspace(*learner.bounds[1], learner.n**0.5)
xys = list(itertools.product(xs, ys))
learner2.add_data(xys, map(ring, xys))
return (learner2.plot().relabel('Homogeneous grid')
+ learner.plot().relabel('With adaptive')
+ learner2.plot(tri_alpha=0.5).relabel('Homogeneous grid')
+ learner.plot(tri_alpha=0.5).relabel('With adaptive')).cols(2)
plots = []
for i in range(100):
N = 10
xs, _ = learner.choose_points(N)
learner.add_data(xs, map(learner.function, xs))
plots.append((learner.n, plot(learner)) |
|
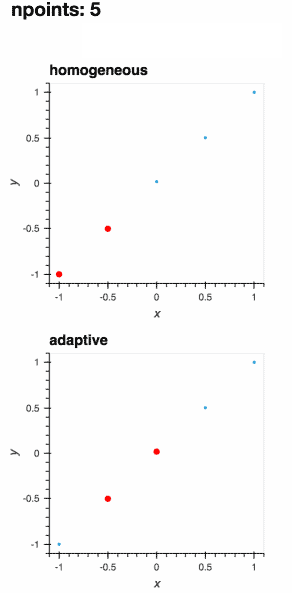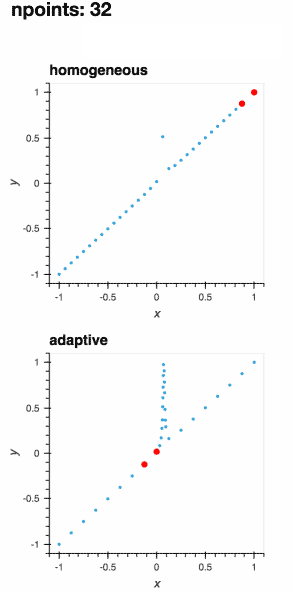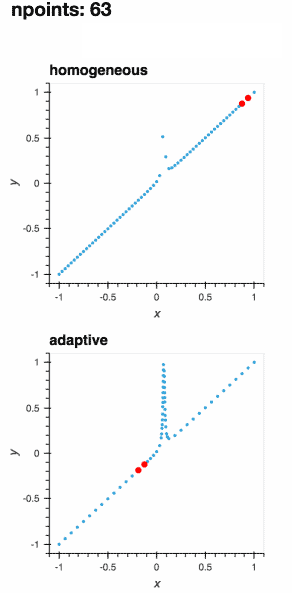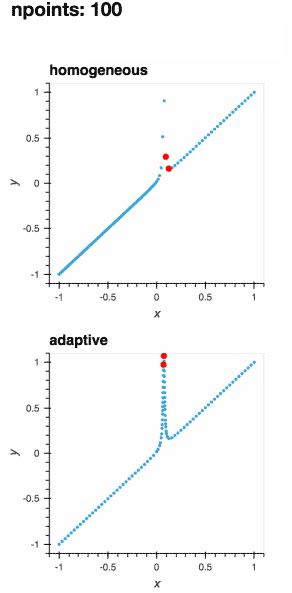
I am going to put this cooler gif in the import adaptive
from functools import partial
import holoviews as hv # Plotting
import numpy as np
adaptive.notebook_extension()
def f(x, offset=0.07357338543088588):
a = 0.01
return x + a**2 / (a**2 + (x - offset)**2)
def plot_loss_interval(learner):
if learner.npoints >= 2:
x_0, x_1 = max(learner.losses, key=learner.losses.get)
y_0, y_1 = learner.data[x_0], learner.data[x_1]
plot = hv.Scatter(([x_0, x_1], [y_0, y_1]))
else:
plot = hv.Scatter([])
return plot.opts(style=dict(size=6, color='r'))
learner = adaptive.Learner1D(f, bounds=(-1, 1))
plots = {0: learner.plot()}
for n in range(1, 101):
xs, _ = learner.choose_points(1)
learner.add_data(xs, map(learner.function, xs))
plots[n] = (learner.plot() * plot_loss_interval(learner))[:, -1.1:1.1]
hm_plots = hv.HoloMap(plots, kdims=['npoints']).relabel('adaptive')
hom_learner = adaptive.Learner1D(f, bounds=(-1, 1), loss_per_interval=adaptive.learner.learner1D.uniform_loss)
hom_plots = {0: hom_learner.plot()}
for n in range(1, 101):
xs, _ = hom_learner.choose_points(1)
hom_learner.add_data(xs, map(hom_learner.function, xs))
hom_plots[n] = (hom_learner.plot() * plot_loss_interval(hom_learner))[:, -1.1:1.1]
hm_hom_plots = hv.HoloMap(hom_plots, kdims=['npoints']).relabel('homogeneous')
(hm_hom_plots + hm_plots).cols(1)Because of |
|
I've added these examples in the docs in b1ebe92. |
|
This is another one: |

The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered: