k8m is an AI-driven Mini Kubernetes AI Dashboard lightweight console tool designed to simplify cluster management. It is built on AMIS and uses kom as the Kubernetes API client. k8m comes with built-in interaction capabilities powered by the Qwen2.5-Coder-7B model and supports integration with your private AI models.
- Compact Design: All functionalities are packed into a single executable file for easy deployment and use.
- User-Friendly: An intuitive user interface and straightforward workflows make Kubernetes management effortless.
- High Performance: Backend built with Golang and frontend based on Baidu AMIS ensure high resource efficiency and fast responsiveness.
- AI-Driven Integration: Provides intelligent support for managing Kubernetes with features like word explanation, resource guide, YAML attribute translation, Describe information interpretation, log AI diagnosis, and command recommendation, integrated with
k8s-gptfor Chinese display. - MCP Integration: Visual management of MCP, enabling large model calls to Tools, with 49 built-in k8s multi-cluster MCP tools, allowing for over a hundred cluster operations. It can serve as an MCP Server for other large model software, facilitating easy management of k8s with large models. Supports mainstream services like mcp.so.
- Multi-Cluster Management: Automatically recognizes clusters using InCluster mode, scans configuration files in the same directory after configuring the kubeconfig path, and registers multiple clusters for management.
- Pod File Management: Enables browsing, editing, uploading, downloading, and deleting files within Pods, simplifying daily operations.
- Pod Operations Management: Supports real-time Pod log viewing, log downloads, and direct Shell command execution within Pods.
- CRD Management: Automatically discovers and manages CRD resources to improve productivity.
- Helm Marketplace: Supports free addition of Helm repositories, one-click installation, uninstallation, and upgrade of Helm applications.
- Cross-Platform Support: Compatible with Linux, macOS, and Windows, and supports various architectures like x86 and ARM for seamless multi-platform operation.
- Fully Open Source: All source code is open without any restrictions, allowing for free customization and extension, and commercial use.
k8m's design philosophy is "AI-driven, lightweight and efficient, simplifying complexity," helping developers and operators quickly get started and effortlessly manage Kubernetes clusters.

- Download: Download the latest version from GitHub.
- Run: Start with the
./k8mcommand and visit http://127.0.0.1:3618. - Parameters:
Usage of ./k8m:
--admin-password string Administrator password (default "123456")
--admin-username string Administrator username (default "admin")
-k, --chatgpt-key string Custom API Key for large models (default "sk-xxxxxxx")
-m, --chatgpt-model string Custom model name for large models (default "Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct")
-u, --chatgpt-url string Custom API URL for large models (default "https://api.siliconflow.cn/v1")
-d, --debug Debug mode
--in-cluster Whether to automatically register and manage the host cluster, enabled by default
--jwt-token-secret string Secret used for generating JWT token after login (default "your-secret-key")
-c, --kubeconfig string Path to kubeconfig file (default "/root/.kube/config")
--kubectl-shell-image string Kubectl Shell image. Default is bitnami/kubectl:latest, must contain kubectl command (default "bitnami/kubectl:latest")
--log-v int Log level for klog.klog.V(2) (default 2)
--login-type string Login method, password, oauth, token, etc., default is password (default "password")
--node-shell-image string NodeShell image. Default is alpine:latest, must contain `nsenter` command (default "alpine:latest")
-p, --port int Listening port (default 3618)
--sqlite-path string Path to sqlite database file (default "./data/k8m.db")
-s, --mcp-server-port int MCP Server listening port, default 3619 (default 3619)
-v, --v Level Log level for klog (default 2)Starting from version v0.0.8, GPT is built-in and does not require configuration. If you need to use your own GPT, please refer to the steps below.
Set the environment variables to enable ChatGPT.
export OPENAI_API_KEY="sk-XXXXX"
export OPENAI_API_URL="https://api.siliconflow.cn/v1"
export OPENAI_MODEL="Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct"If setting parameters does not work, try using ./k8m -v 6 to get more debugging information.
The following information will be output, check the logs to confirm whether ChatGPT is enabled.
ChatGPT enabled status:true
ChatGPT enabled key:sk-hl**********************************************, url:https://api.siliconflow.cn/v1
ChatGPT uses model set in environment variables:Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-7B-InstrucThis project integrates the github.com/sashabaranov/go-openai SDK. For users in China, it's recommended to use the Silicon Flow service. After logging in, create an API_KEY at https://cloud.siliconflow.cn/account/ak.
Below is a table of environment variable settings supported by k8m and their functions:
| Environment Variable | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
PORT |
3618 |
Listening port number |
MCP_SERVER_PORT |
3619 |
Listening port number for built-in multi-cluster k8s MCP Server |
KUBECONFIG |
~/.kube/config |
Path to kubeconfig file |
OPENAI_API_KEY |
"" |
API Key for large models |
OPENAI_API_URL |
"" |
API URL for large models |
OPENAI_MODEL |
Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct |
Default model name for large models, set to deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B if needed |
LOGIN_TYPE |
"password" |
Login method (e.g., password, oauth, token) |
ADMIN_USERNAME |
"admin" |
Administrator username |
ADMIN_PASSWORD |
"123456" |
Administrator password |
DEBUG |
"false" |
Whether to enable debug mode |
LOG_V |
"2" |
Log output level, same usage as klog |
JWT_TOKEN_SECRET |
"your-secret-key" |
Secret used for generating JWT Token |
KUBECTL_SHELL_IMAGE |
bitnami/kubectl:latest |
kubectl shell image address |
NODE_SHELL_IMAGE |
alpine:latest |
Node shell image address |
SQLITE_PATH |
/data/k8m.db |
Persistent database address, default sqlite database, file address /data/k8m.db |
IN_CLUSTER |
"true" |
Whether to automatically register and manage the host cluster, enabled by default |
These environment variables can be set when running the application, for example:
export PORT=8080
export OPENAI_API_KEY="your-api-key"
export GIN_MODE="release"
./k8mNote: Environment variables will be overridden by startup parameters.
Use KinD or MiniKube to install a small k8s cluster.
- Create KinD Kubernetes Cluster
brew install kind
- Create a new Kubernetes cluster:
kind create cluster --name k8sgpt-demo
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/weibaohui/k8m/refs/heads/main/deploy/k8m.yaml
- Access: NodePort is used by default, please access port 31999. Or configure Ingress yourself. http://NodePortIP:31999
It is recommended to modify through environment variables first. For example, add env parameters in deploy.yaml.
Suitable for MCP tool integration like Cursor, Claude Desktop, Windsurf, etc. You can also use these software's UI to add configurations.
{
"mcpServers": {
"kom": {
"type": "sse",
"url": "http://IP:9096/sse"
}
}
}- Open Claude Desktop settings panel
- Add MCP Server address in API configuration section
- Enable SSE event listening
- Verify connection status
- Enter Cursor settings interface
- Find extension service configuration
- Add MCP Server URL (e.g. http://localhost:3619/sse)
- Access configuration center
- Set API server address
- Ensure MCP Server is running with accessible ports
- Check network connectivity
- Verify SSE connection establishment
- Check tool logs for troubleshooting (failed MCP executions will have error records)
MCP program uses port 3619. NodePort uses port 31919. If started in binary mode, the access address is http://ip:3619/sse If started in cluster mode, the access address is http://nodeIP:31919/sse
The management scope of the built-in MCP Server is consistent with the cluster scope managed by k8m. All connected clusters in the interface can be used.
| Category | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cluster Management (1) | list_clusters |
List all registered Kubernetes clusters |
| Deployment Management (12) | scale_deployment |
Scale Deployment |
restart_deployment |
Restart Deployment | |
stop_deployment |
Stop Deployment | |
restore_deployment |
Restore Deployment | |
update_tag_deployment |
Update Deployment image tag | |
rollout_history_deployment |
Query Deployment upgrade history | |
rollout_undo_deployment |
Rollback Deployment | |
rollout_pause_deployment |
Pause Deployment upgrade | |
rollout_resume_deployment |
Resume Deployment upgrade | |
rollout_status_deployment |
Query Deployment upgrade status | |
hpa_list_deployment |
Query HPA list of Deployment | |
list_deployment_pods |
Get Pod list managed by Deployment | |
| Dynamic Resource Management (including CRD, 8) | get_k8s_resource |
Get k8s resource |
describe_k8s_resource |
Describe k8s resource | |
delete_k8s_resource |
Delete k8s resource | |
list_k8s_resource |
List k8s resources in list form | |
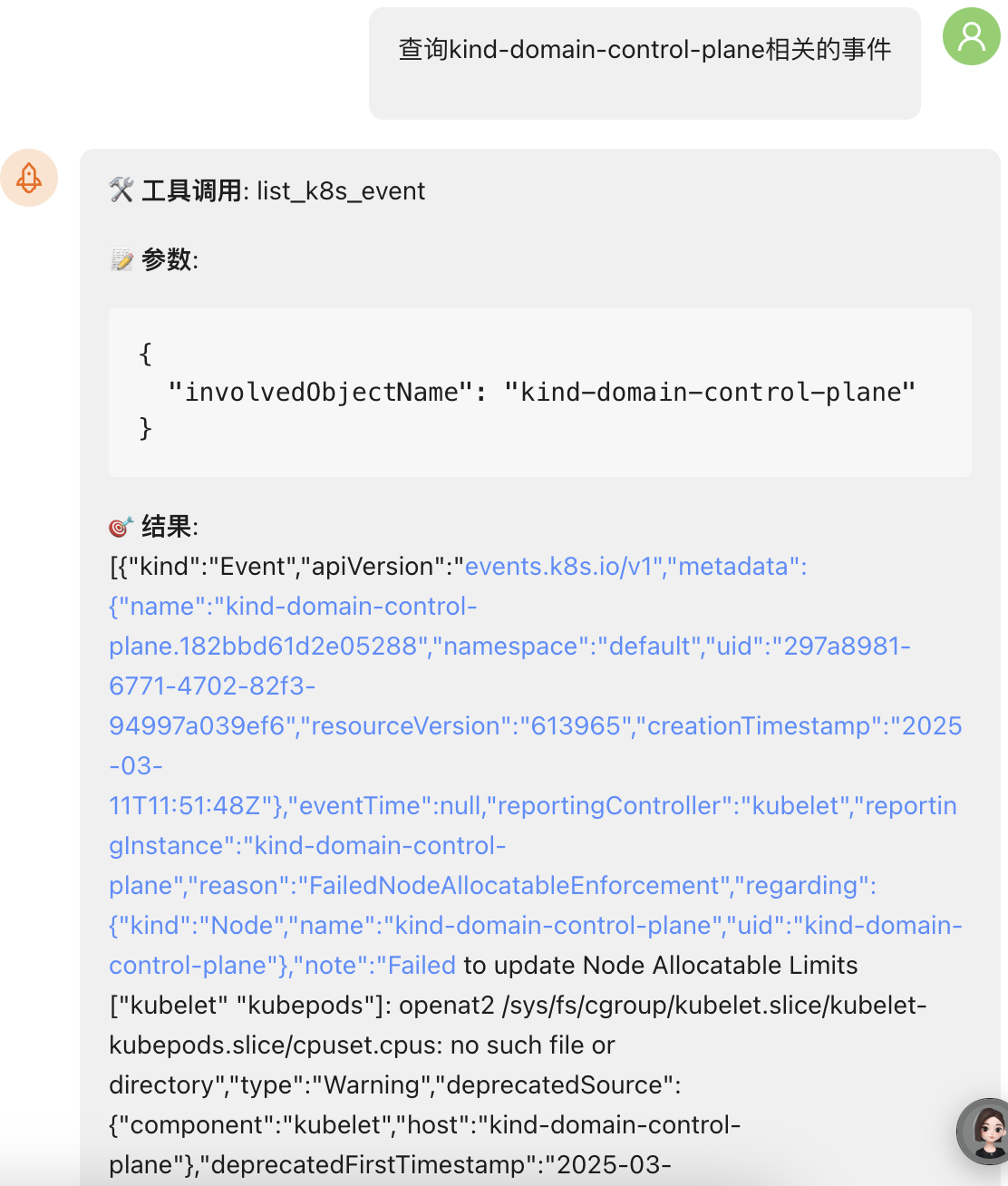
list_k8s_event |
List k8s events in list form | |
patch_k8s_resource |
Update k8s resource using JSON Patch | |
label_k8s_resource |
Add or delete labels for k8s resources | |
annotate_k8s_resource |
Add or delete annotations for k8s resources | |
| Node Management (8) | taint_node |
Add taint to node |
untaint_node |
Remove taint from node | |
cordon_node |
Set Cordon for node | |
uncordon_node |
Cancel Cordon for node | |
drain_node |
Execute Drain for node | |
get_node_resource_usage |
Query resource usage of node | |
get_node_ip_usage |
Query Pod IP resource usage on node | |
get_node_pod_count |
Query Pod count on node | |
drain_node |
Execute Drain for node | |
get_node_resource_usage |
Query resource usage of node | |
get_node_ip_usage |
Query Pod IP resource usage on node | |
get_node_pod_count |
Query Pod count on node | |
| Pod Management (14) | list_pod_files |
List Pod files |
list_all_pod_files |
List all Pod files | |
delete_pod_file |
Delete Pod file | |
upload_file_to_pod |
Upload file to Pod, supports passing text content and storing as Pod file | |
get_pod_logs |
Get Pod logs | |
run_command_in_pod |
Execute command in Pod | |
get_pod_linked_service |
Get Service linked to Pod | |
get_pod_linked_ingress |
Get Ingress linked to Pod | |
get_pod_linked_endpoints |
Get Endpoints linked to Pod | |
get_pod_linked_pvc |
Get PVC linked to Pod | |
get_pod_linked_pv |
Get PV linked to Pod | |
get_pod_linked_env |
Get runtime environment variables of Pod by running env command in Pod | |
get_pod_linked_env_from_yaml |
Get runtime environment variables of Pod from Pod yaml definition | |
get_pod_resource_usage |
Get resource usage of Pod, including CPU and memory request values, limit values, allocatable values, and usage ratios | |
| YAML Management (2) | apply_yaml |
Apply YAML resource |
delete_yaml |
Delete YAML resource | |
| Storage Management (3) | set_default_storageclass |
Set default StorageClass |
get_storageclass_pvc_count |
Get PVC count under StorageClass | |
get_storageclass_pv_count |
Get PV count under StorageClass | |
| Ingress Management (1) | set_default_ingressclass |
Set default IngressClass |
v0.0.66 Update
- Added MCP support
- Built-in multi-cluster operations:
- list_k8s_resource
- get_k8s_resource
- delete_k8s_resource
- describe_k8s_resource
- get_pod_logs
v0.0.67 Update
- New MCP event query tool
- New cluster registration query tool
- Enhanced label-based resource filtering (e.g. app=k8m)
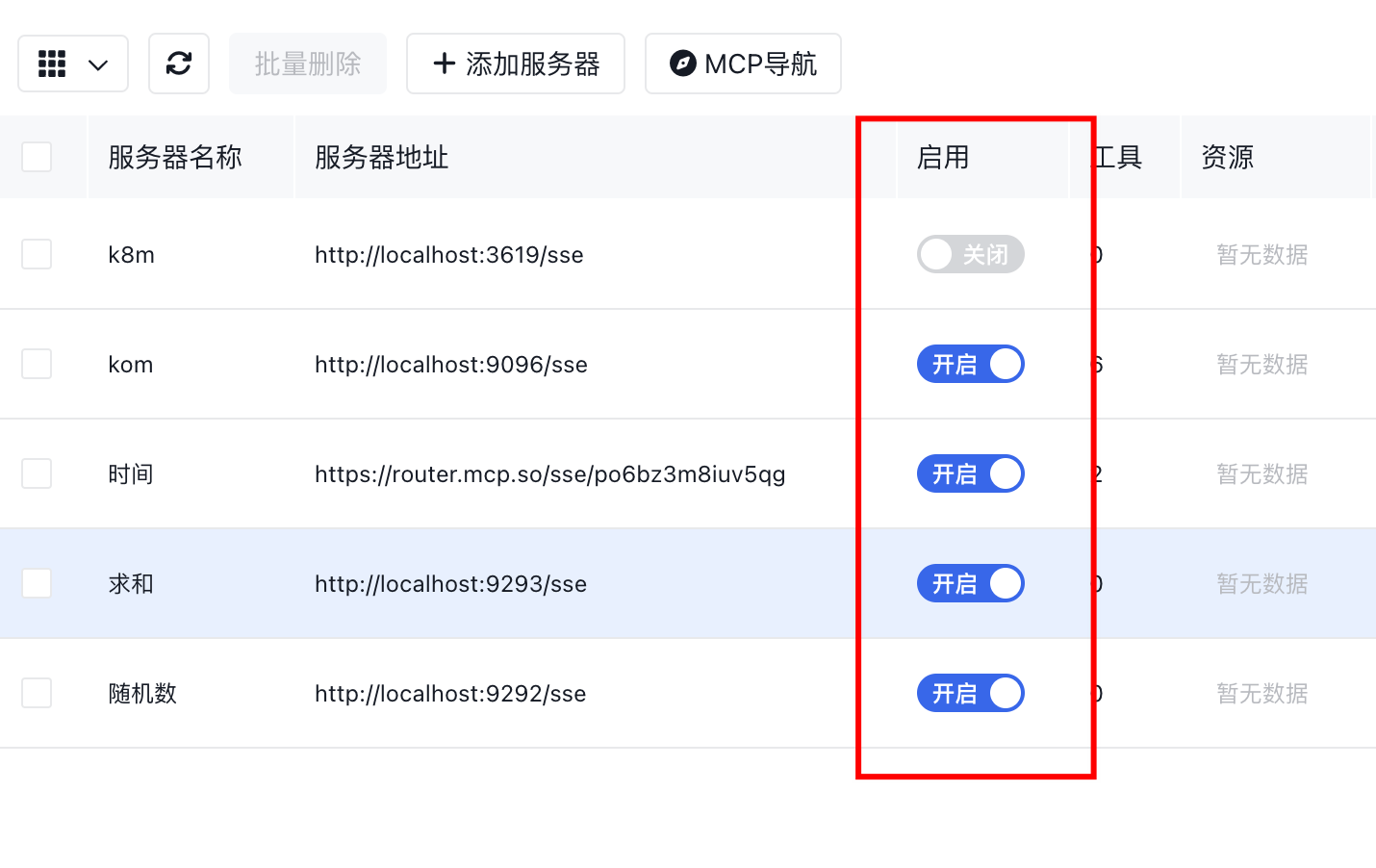
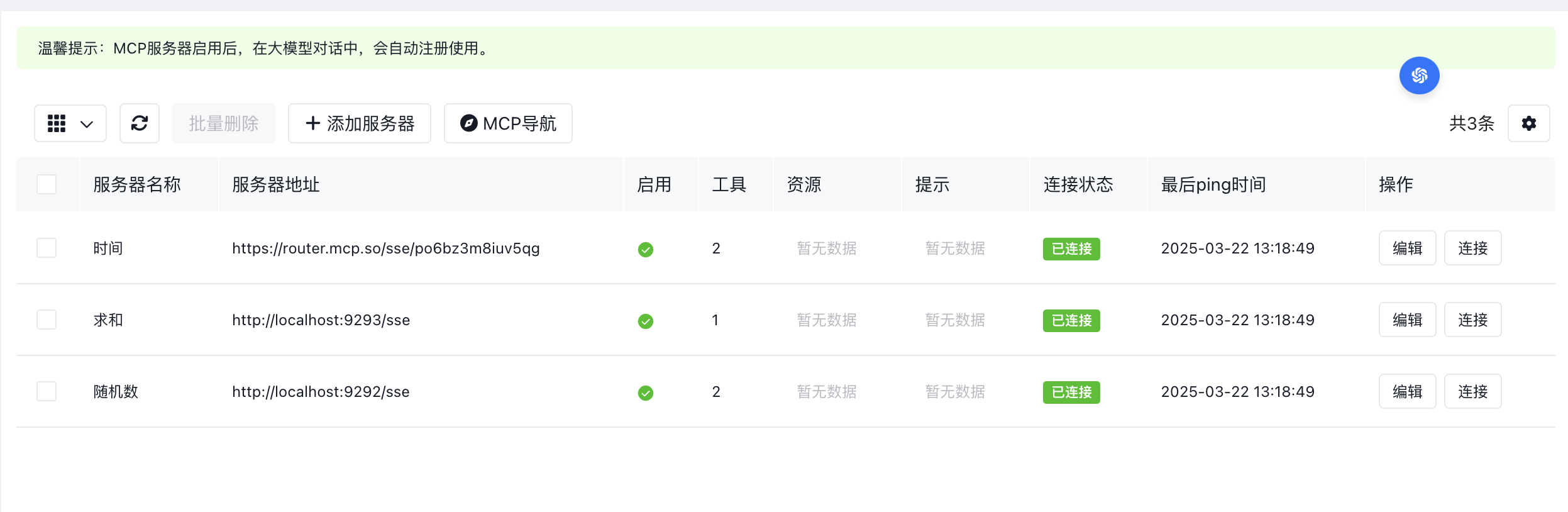
- Added quick enable/disable toggle for MCP Server
v0.0.64 Update